Configuring Clusters (Legacy)
This page includes instructions for configuring our legacy cloud clusters. To read about the difference between these clusters and our next-generation clusters, please see this page.
Accessing Configuration Settings
You can access a resource’s configuration settings from the Home page. Navigate to the Computing Resources module and click the gear icon for the resource you want to configure.
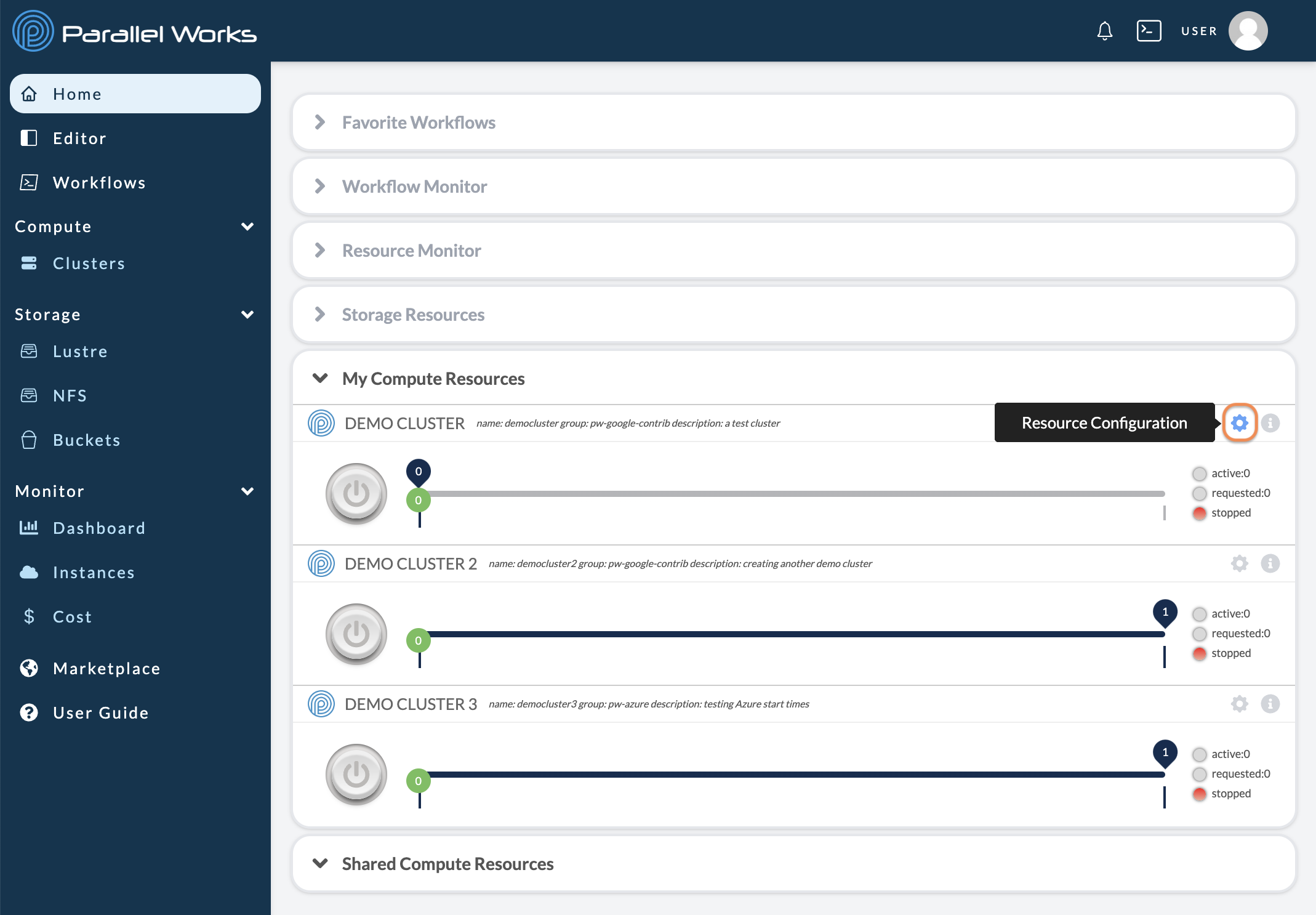
Alternatively, you can navigate to the Clusters page and click the name of the resource you want to configure.
About the Resource Configuration Page
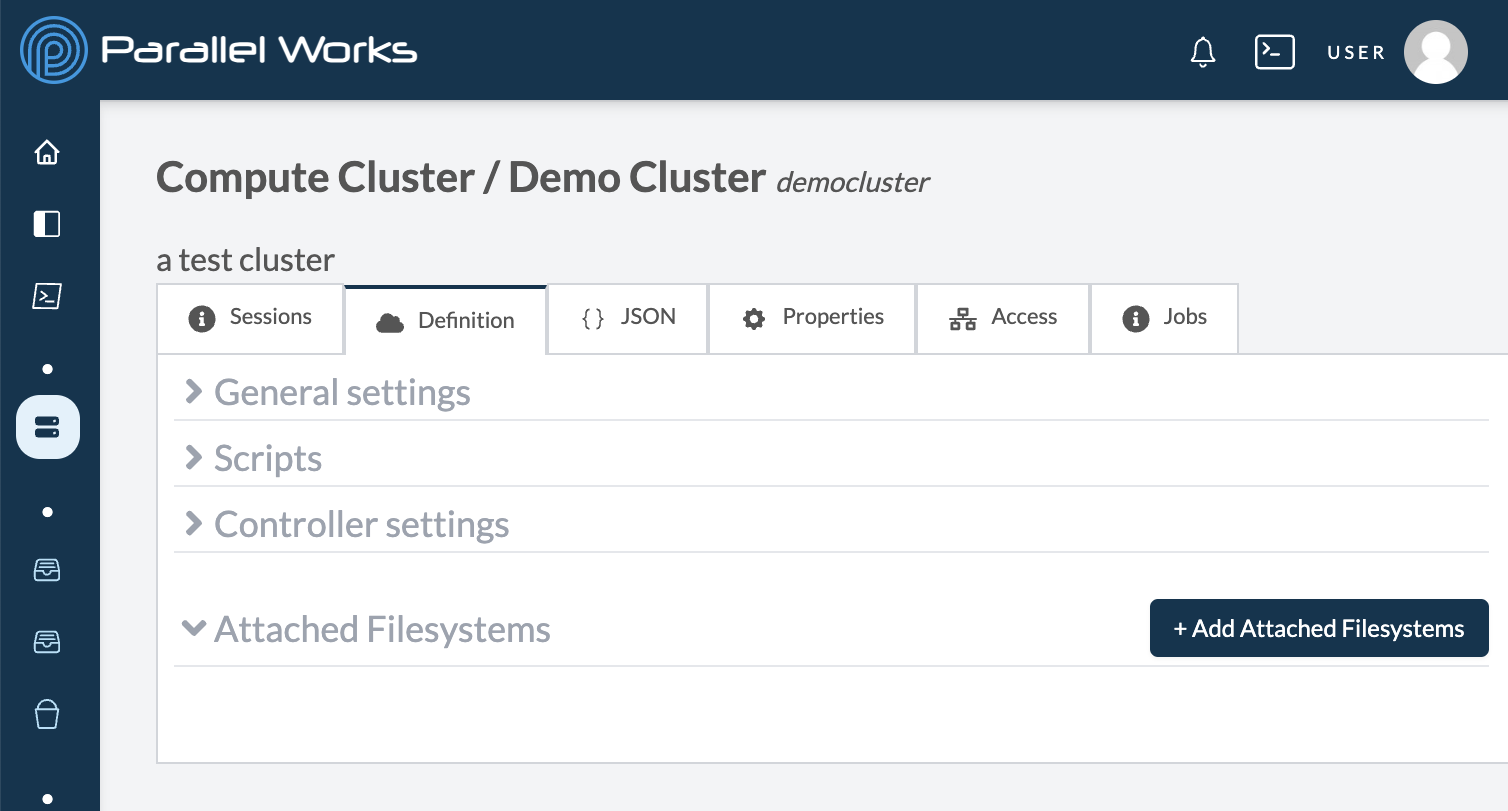
When you navigate to a cluster's configuration settings, there are four tabs for customization.
Sessions
By default, you’ll see the Sessions tab when you navigate to configuration settings. This tab shows your previous cluster sessions well as provisioning and deletion logs.
In the Sessions module of this tab, you’ll also be able to see sessions for any attached ephemeral storage resources. If multiple ephemeral storage resources are attached to the cluster, you’ll see a dropdown to select when ephemeral storage logs you’d like to see. The deletion logs for ephemeral storage resources are combined with the cluster deletion logs.
For more information, please see Storage Types.
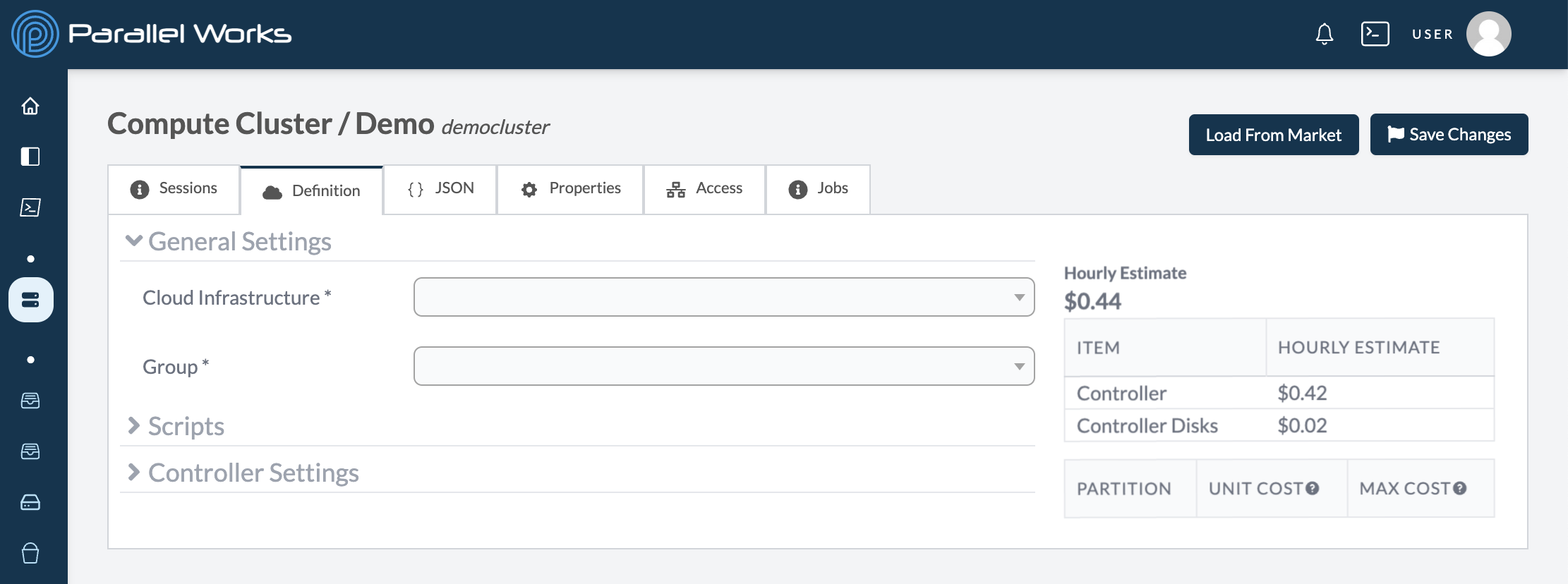
Definition
Use this tab to adjust your cluster's parameters. For more information, see General Settings below.
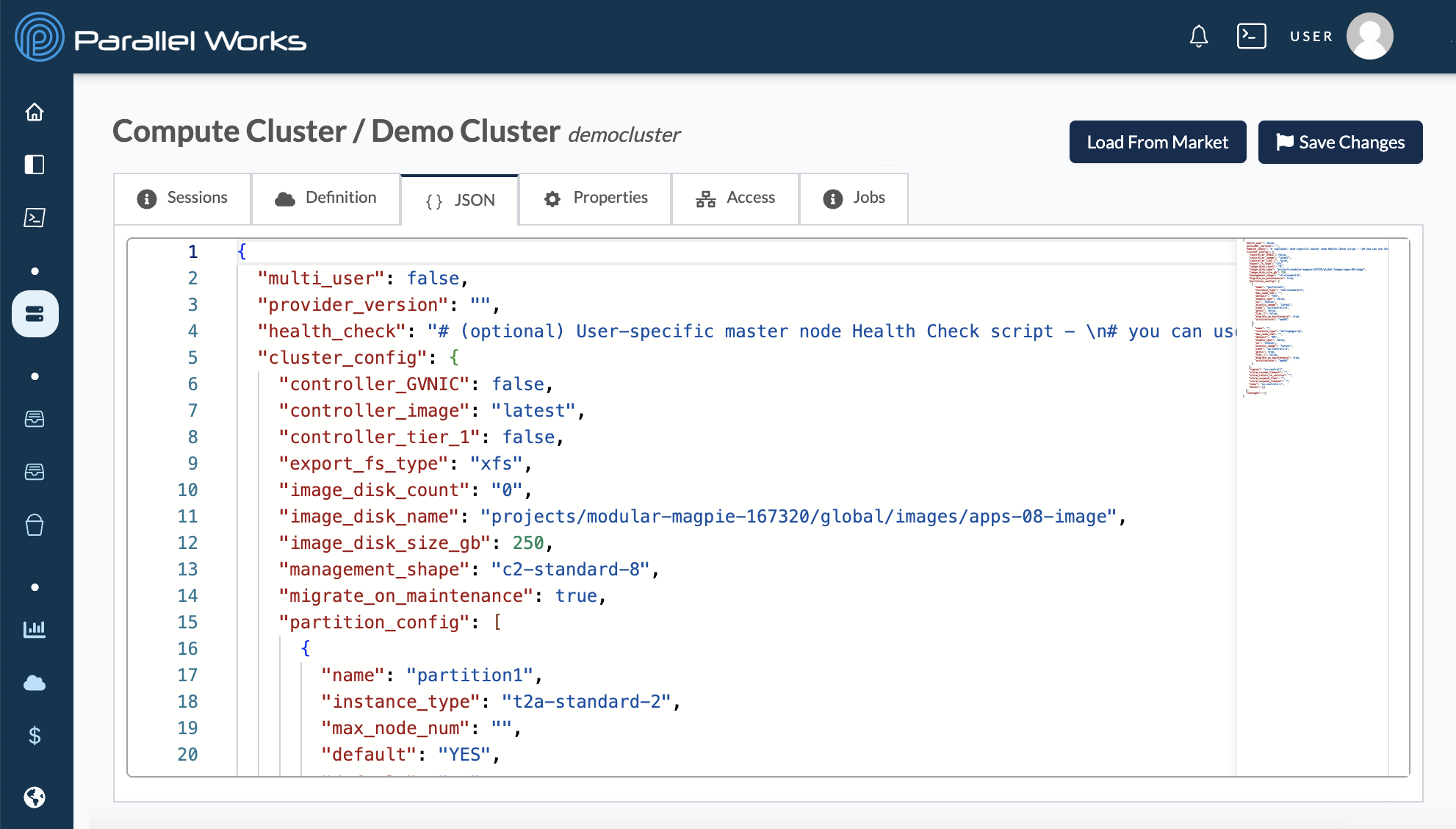
JSON
This tab shows the code version of your resource’s configuration settings. You can manually adjust the parameters seen in the Definition tab.
Properties
Use this tab to adjust the display settings of your cluster, including the name, display name, description, tags, and thumbnail.
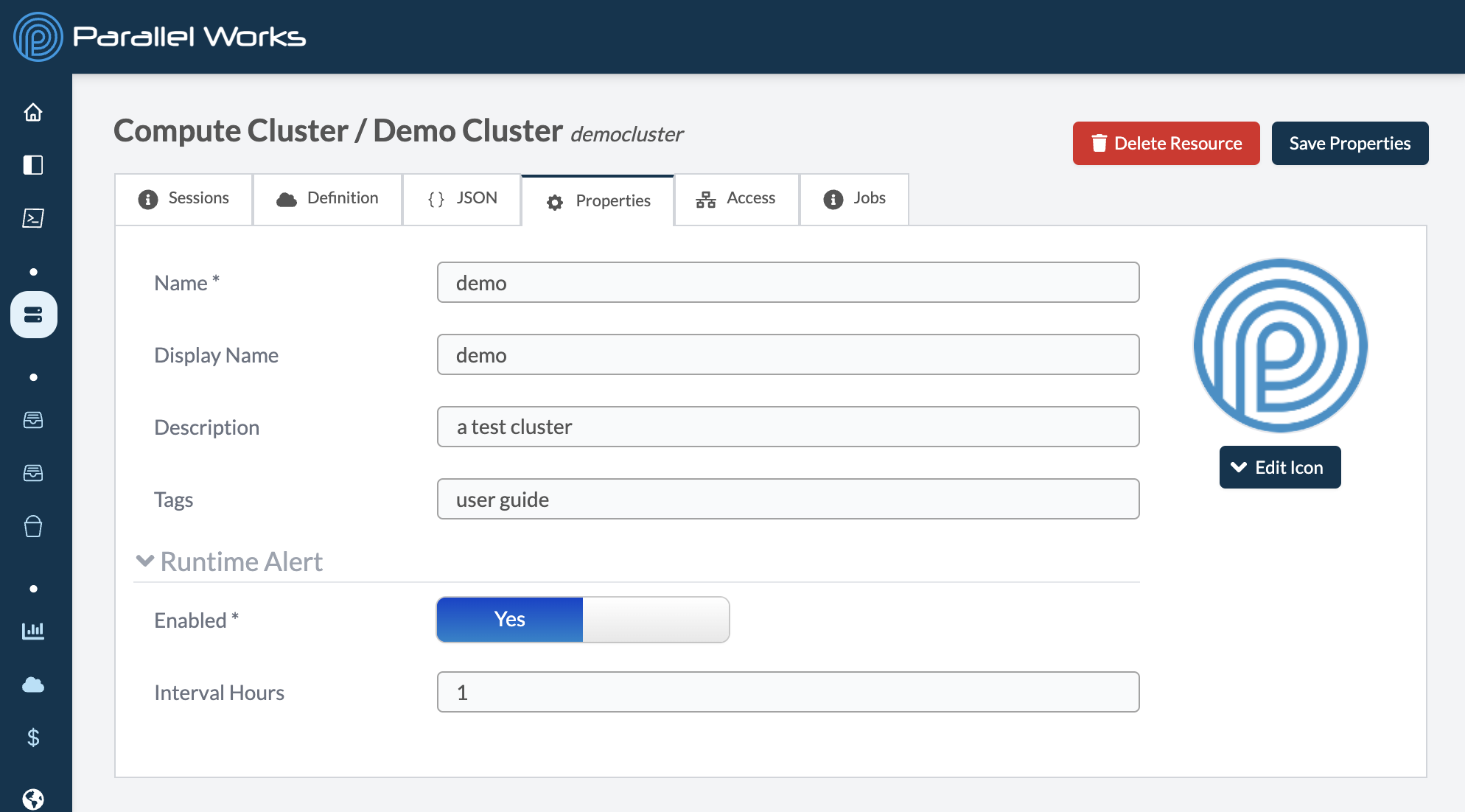
You can also enable automated alert emails from noreply@parallelworks.com by clicking the Enabled toggle button. The field for Interval Hours will appear, and the value you enter here determines how often you'll receive run time alerts.
Access
Use this tab to manage which groups can access your cluster. Your group name(s) will be specific to your organization. For more information, please see Group below.
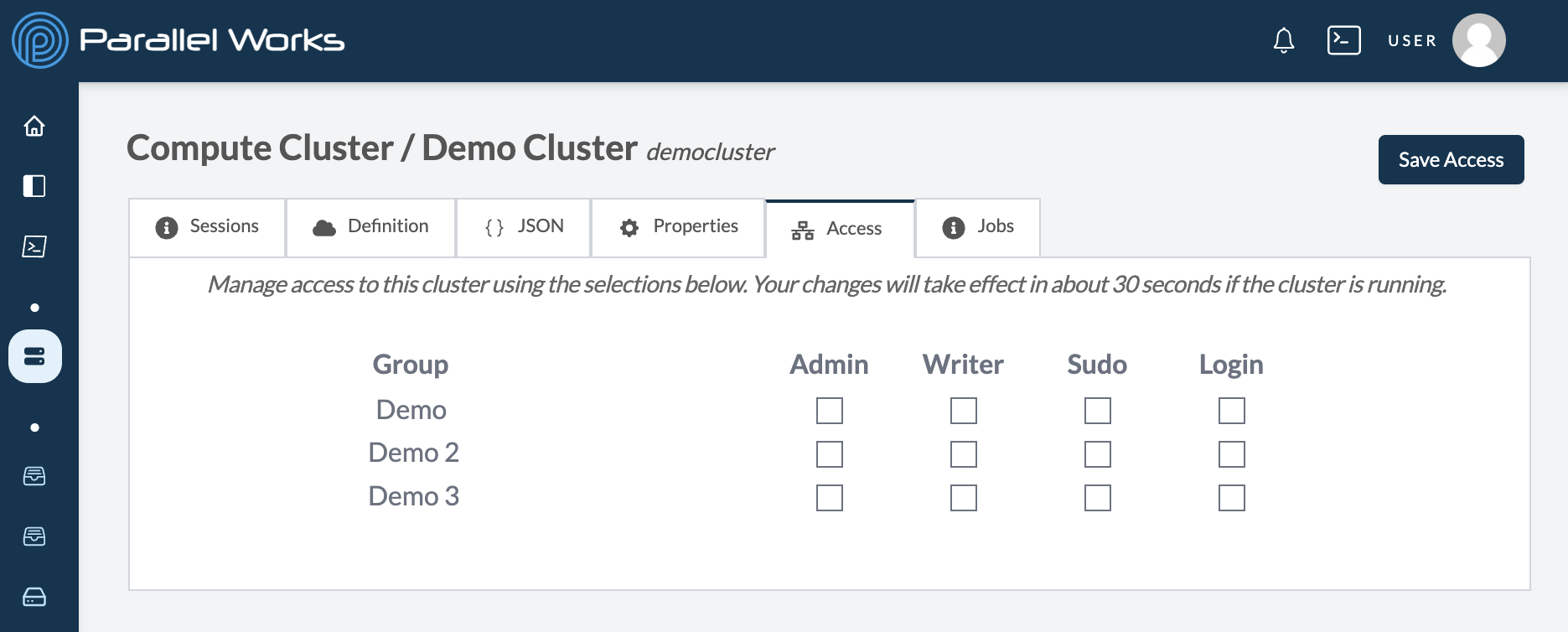
There are four levels of access:
- Admin grants users the same level of access as the owner of the cluster, including the ability to delete it.
- Writer grants users the ability to edit the cluster’s configuration as well as log in to the cluster.
- Sudo grants users the ability to log in to the cluster with root access via the
sudocommand. Root access allows users to do anything inside both the controller and compute nodes. - Login grants users the ability to log in to any compute node on the cluster by using the
sshcommand. Users' home directories are created automatically on the first login. Removing this permission revokes access after 30 seconds and kills any active sessions.
Although you can remove sudo access, you should still consider a cluster to be compromised if others users have had that access. It is best to recreate a cluster rather than using the one that previously had shared sudo access.
Live updatable settings
Some settings are updatable while the cluster is running. These settings are marked with a Live Updatable icon.
General Settings
Clusters will typically have these settings in the Definition tab of the configuration page.
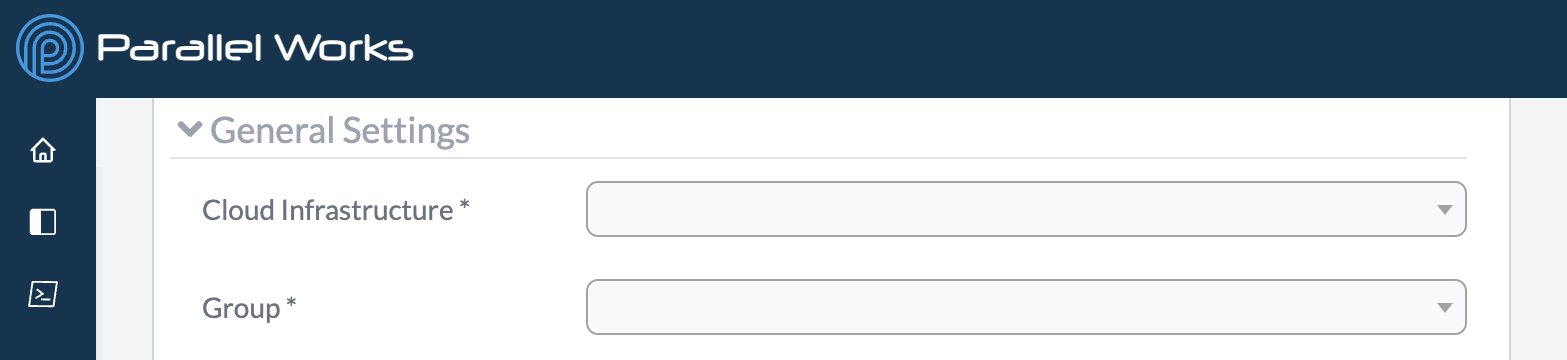
Cloud Infrastructure
Use this dropdown menu to select the base infrastructure that your organization uses for a specific cloud service provider. If you're not sure which one to select, please contact your organization's administrator.
Group
Use this dropdown menu to select the group name that your organization uses to allocate costs. This menu is especially important if your organization is running multiple groups simultaneously.
If you’re not sure which group to select, you can contact us or your organization’s ACTIVATE administrator.
Script Settings
Optionally, you can set scripts to execute when you start a cluster.
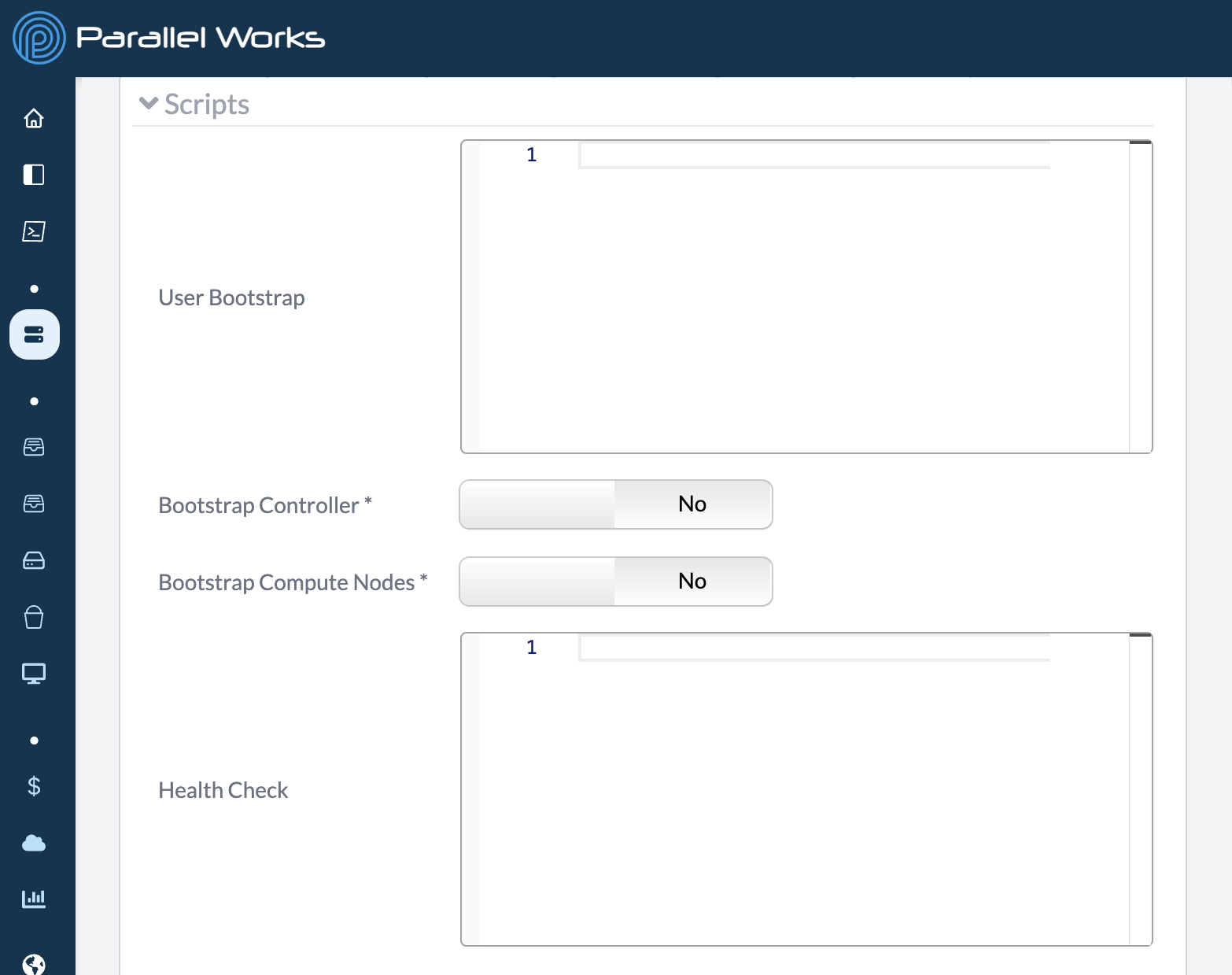
User Bootstrap
Use this text box to set a script that executes once a controller node has started. For example, you can set files to automatically move into a specific folder.
Bootstrap Controller
Use this toggle button to specify whether your bootstrap script will run on the controller node.
Bootstrap Compute Nodes
Use this toggle button to specify whether your bootstrap script will run on the compute node(s).
Health Check
Use this text box to set a script that runs a health check on a controller node. When the script is done running, you’ll see any error codes in red or an exit code of 0 in green if there are no errors.
For more information, see Health Checks (coming soon).
Controller Settings
These settings define the configuration for the controller node, such as region, instance type, and OS image. Some settings will differ depending on which type of resource you’re using. For more information, see CSP-Specific Settings below.
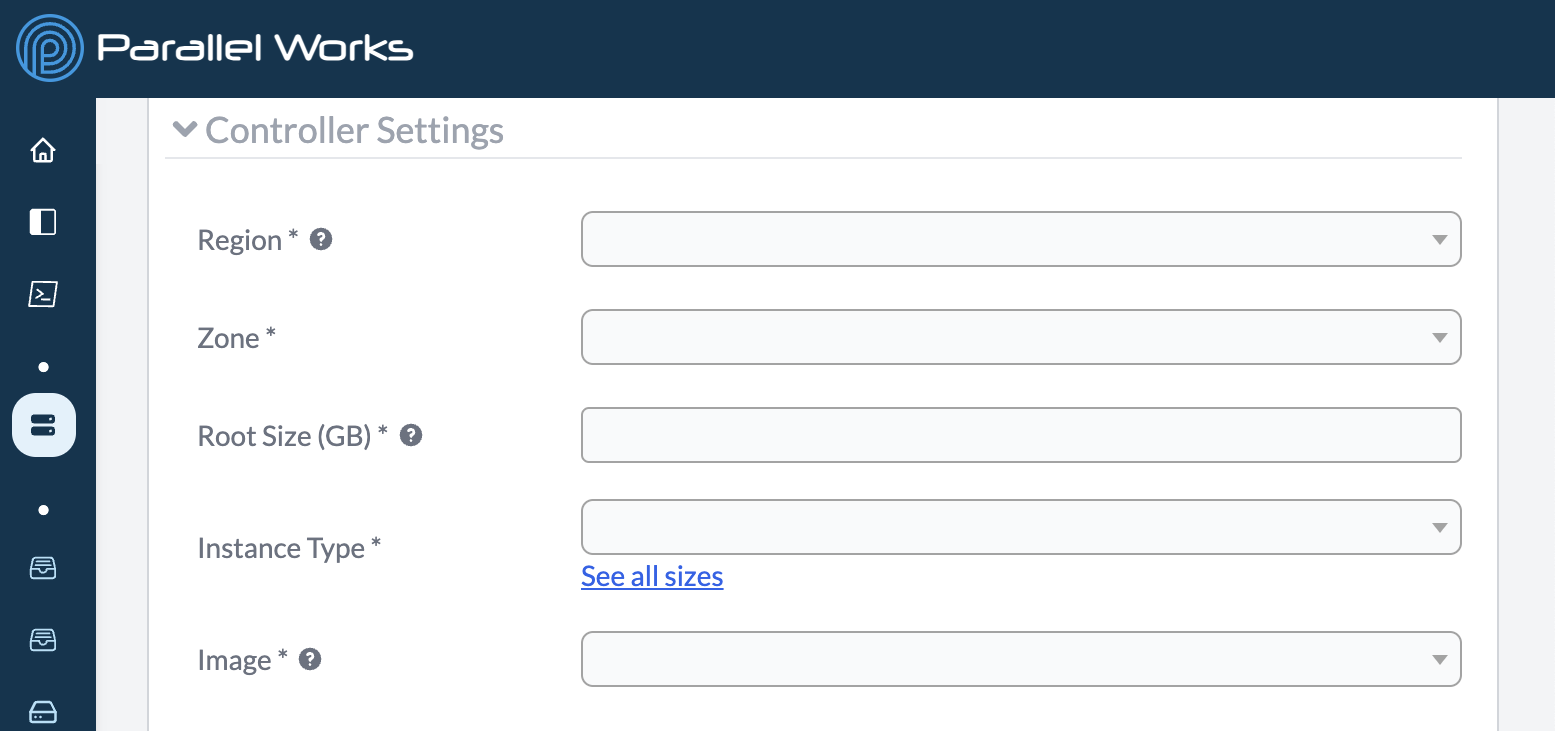
Region
Use this dropdown menu to select the region that your cluster will deploy computing resources into.
A region represents a geographic area.
Zone
Use this dropdown menu to select the zone to use for the controller.
A zone refers to an isolated location inside a region.
Azure clusters do not have a Zone menu.
Root Size (GB)
Use this field to specify the size of the root disk in gigabytes (GB).
Instance Type
Use this dropdown menu to select the instance type of the controller. The instance type determines the CPUs and amount of memory available on the machine. Certain instance types may also have specialty hardware, such as GPUs or low-latency networking options.
To see a list of avaialable instance types and their cost per hour, click See all sizes. From the instance type list, you can click an option to select it.
For more information about instance types and what they mean, please see Choosing Instance Types.
Image
Use this dropdown menu to select the operating system (OS) image for the cluster's controller node.
If you're not sure which image to pick, we recommend using the latest version because this will ensure you have the most up-to-date software on your cluster; the latest image version includes OS updates and software required to connect to ACTIVATE.
You can also use this dropdown menu to select custom cloud snapshots.
Partition Settings Live Updatable
You can create partitions in clusters to send your work to differently configured sets of worker nodes. Partitions are especially useful if you’re working on a project that needs more or fewer nodes for specific tasks (for example, if you were running a simulation model and only a small dataset required twice the amount of GPU power to render properly).
You must have at least one partition in your cluster.
If you click + Add Partition, a list of new settings will appear. Typically, a partition will have the following configuration options. Some settings will differ depending on which type of resource you’re using. For more information, see CSP-Specific Settings below.
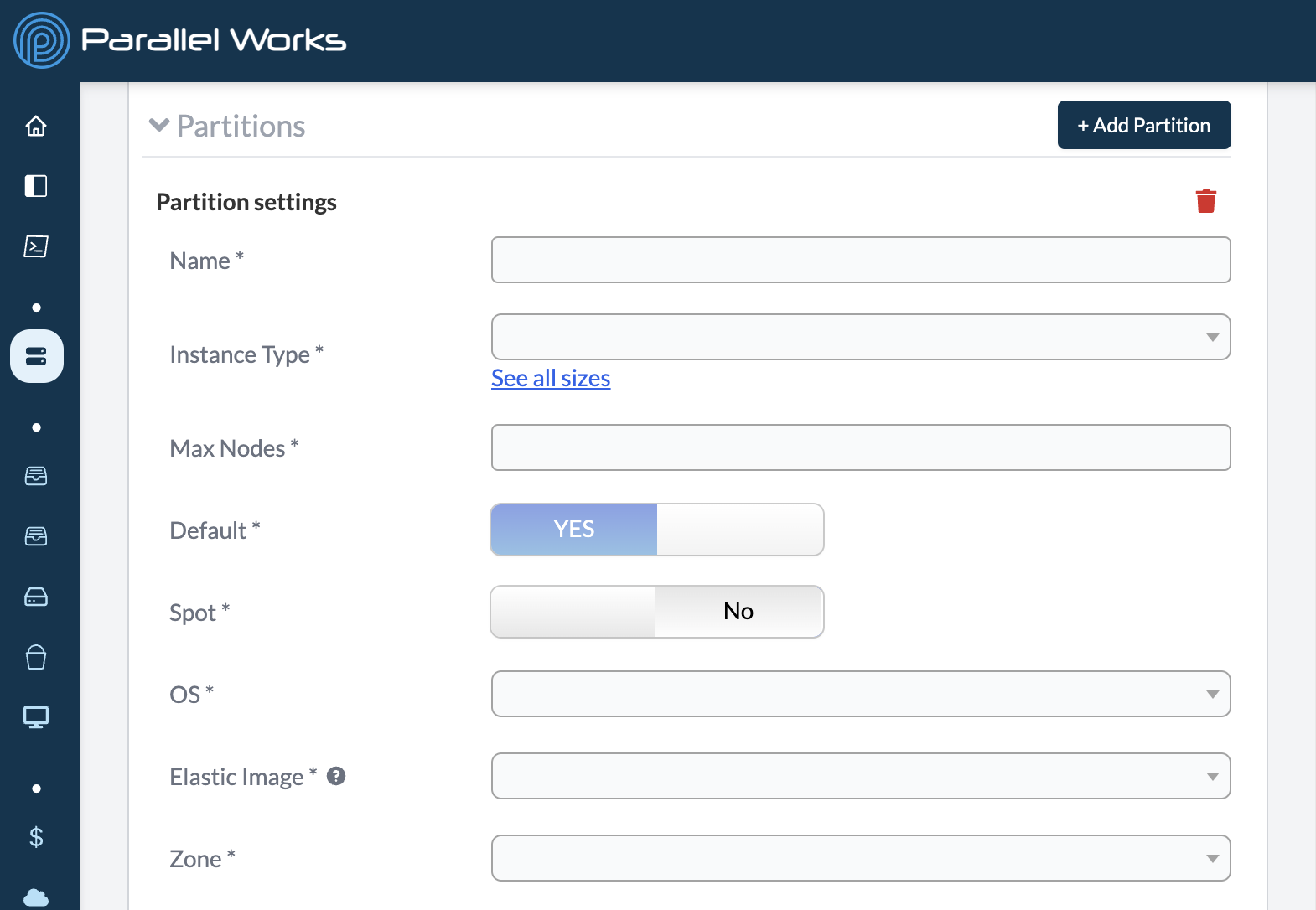
Name
Use this field to name your partition. Be sure to use a unique name for each partition you create. Your partition should never be named default.
Instance Type
Use this dropdown menu to select the configuration of the partition. These options work in the same way that the controller instance types do.
Max Nodes
Use this field to enter the max number of nodes in a partition.
Default
Use this toggle button to specify whether a partition is the default location for running jobs. For more information on running jobs on specific partitions, see Submitting Jobs.
This feature is important if you create multiple partitions. If you only create one partition, it will automatically be set to Default and cannot be changed, as shown in the screenshot above.
Spot
Use this toggle button to specify whether a partition is a spot instance. Spot instances can be cost effective because they make use of resources that are already available but currently unused.
However, spot instances can be disrupted because another user can take over that available resource at any time. For this reason, we recommend using spot instances at your own risk.
OS
Use this dropdown menu to select the operating system (OS) for your partition. This option should match the OS selected for Elastic Image.
Elastic Image
Use this dropdown menu to select the operating system image for the partition. We recommend using the latest version.
Zone
Use this dropdown menu to select the zone within your selected region.
Your partition's zone must be the same as your controller's zone.
Slurm Settings
ACTIVATE uses Slurm to manage jobs on controller and compute nodes. The settings below determine how Slurm behaves for your cluster's nodes.
Please note that numerical values you enter in these fields are measured in seconds.
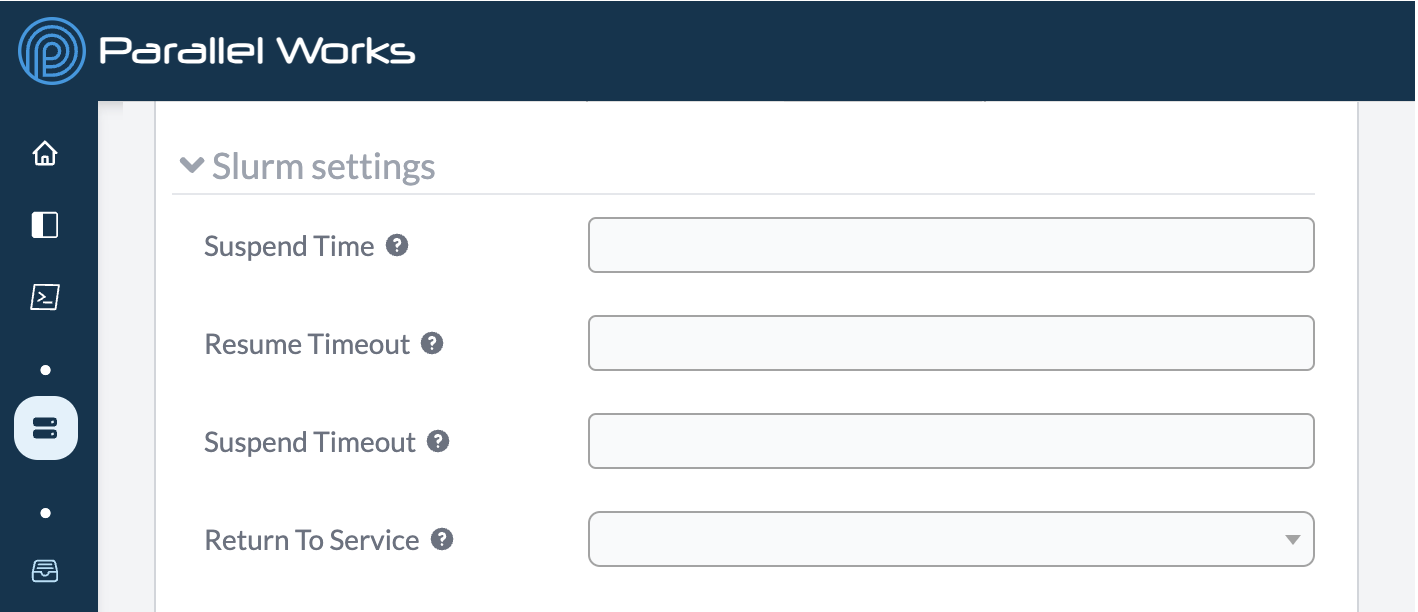
Suspend Time
Use this field to set how long Slurm will wait before shutting down idle nodes. This field is set to 300 by default.
Resume Timeout
Use this field to set the maximum amount of time Slurm will try to start nodes. If the nodes don’t start by the end of the set time, Slurm will end the initialization attempt. This field is set to 1200 by default.
Suspend Timeout
Use this field to set how long Slurm will wait to make nodes available again after shutting them down. This field is set to 300 by default.
Return To Service
Use this dropdown menu to select when down nodes are returned to service.
The Non Responsive option means that down nodes will become available only if they were set to down because they were non-responsive.
The Any Reason option means that down nodes will become available if they were set to down for any reason, including low memory, an unexpected reboot, or being non-responsive.
This field is set to Non Responsive by default.
Attached Filesystems Settings
Use this section to attach any of your configured storage resources. For more information, please see Attaching Storage.
CSP-Specific Settings
Each cloud service provider (CSP) builds and configures their resources differently. Clusters on ACTIVATE have settings that correspond to each CSP’s model of cloud services. The CSP-specific parameters are outlined below.
Please note that these CSP-specific settings will also appear as options inside the partition settings on clusters.
AWS
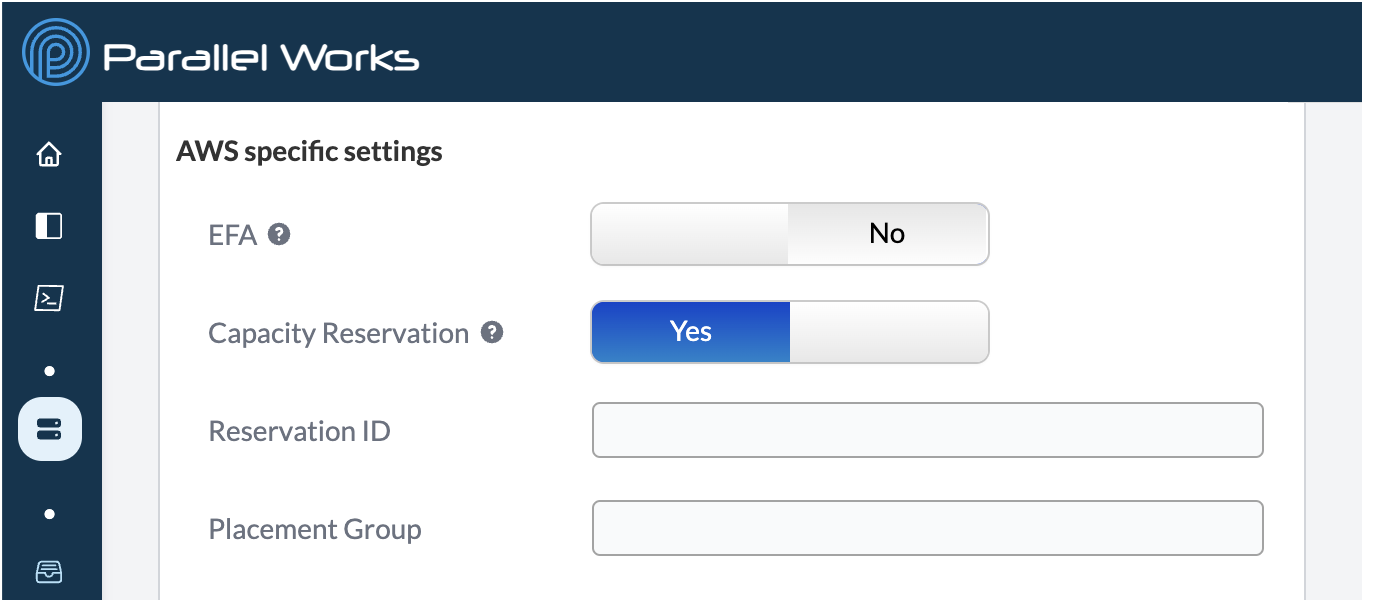
EFA
Use this toggle button to enable Elastic Fabric Adapter (EFA), which improves inter-instance network performance. EFA is useful if you need to scale HPC or machine-learning applications to thousands of CPUs or GPUs.
Please note that EFA is not supported on all instance types.
For more information and a list of supported instance types, see the AWS documentation on EFA.
Capacity Reservation*
Use this toggle button to enable on-demand capacity reservations, which reserve a set amount of compute capacity. When Capacity Reservation is enabled, two new fields will appear: Reservation ID and Placement Group. These identifiers come directly from AWS.
Before you can use a capacity reservation on ACTIVATE, it must first be configured on AWS Cloud by an administrator in your organization. After this initial step, your administrator can distribute the values for Reservation ID and Placement Group.
*This setting is only available on AWS partitions, not on AWS controllers.
Azure
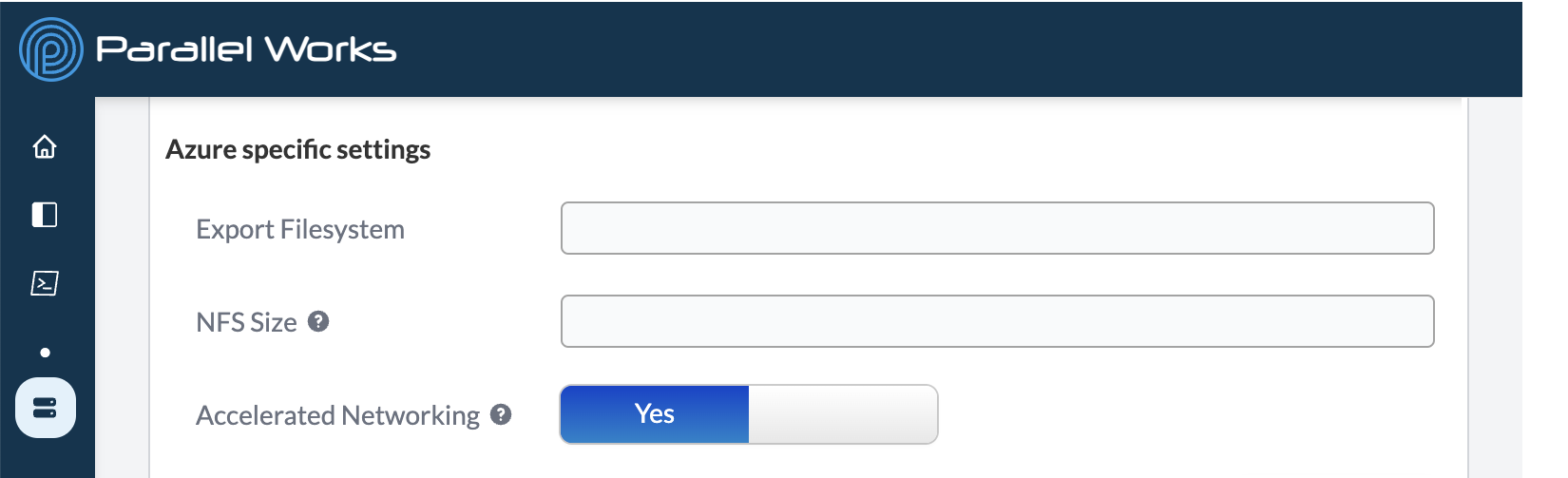
Export Filesystem
Use this field to enter the name of a network filesystem (NFS), which is an existing system on an external device that’s available for read and/or write access on your cluster.
If you want to set up an NFS, please contact us or your ACTIVATE administrator.
NFS Size
Use this field to enter the size of your NFS.
Please note that the values for NFS Size and Image Disk Size must be the same.
Accelerated Networking
Use this toggle button to enable accelerated networking, which improves networking performance for large workloads on multiple cloud clusters.
For more information, see the Azure documentation on accelerated networking.
Google
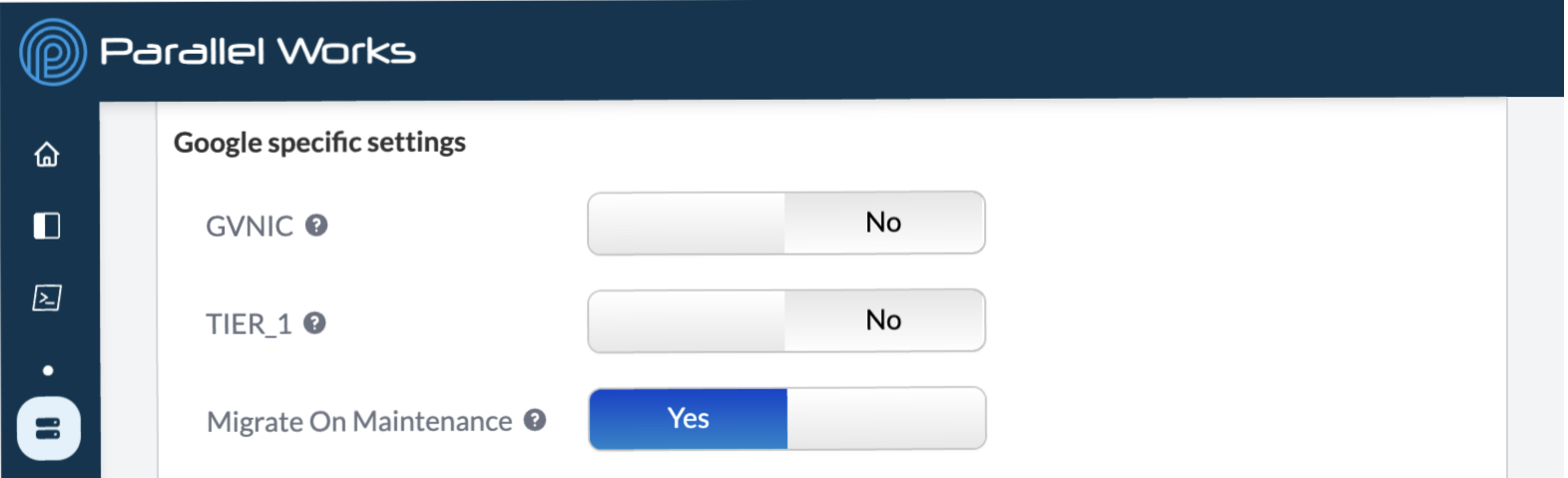
GVNIC
Use this toggle button to enable Google Virtual Network Interface Card (gVNIC), which supports higher network bandwidths from 50–100 Gbps.
Please note that gVNIC is not supported on all instance types.
For more information and a list of supported instance types, see the Google documentation on gVNIC.
TIER_1
Use this toggle button to enable Tier_1, which increases maximum egress bandwidth (upload speed) to 50–100 Gps, depending on the size of the instance. If Tier_1 is off, the egress bandwidth will range from 10–32 Gbps.
Please note that Tier-1 is only supported if gVNIC is also active. If you try to start Tier-1 by itself, you'll see the error message Tier_1 is only supported if gVNIC is on.
For more information, see the Google documentation on Tier_1.
Migrate On Maintenance
This toggle button enables live migration whenever the virtual machine’s host undergoes maintenance, meaning that Google will migrate the virtual machine to another host without any downtime.
Please note that GPU and spot instances cannot be live migrated. When supported, we recommend turning this feature on.
For more information, see the Google documentation on live migration.
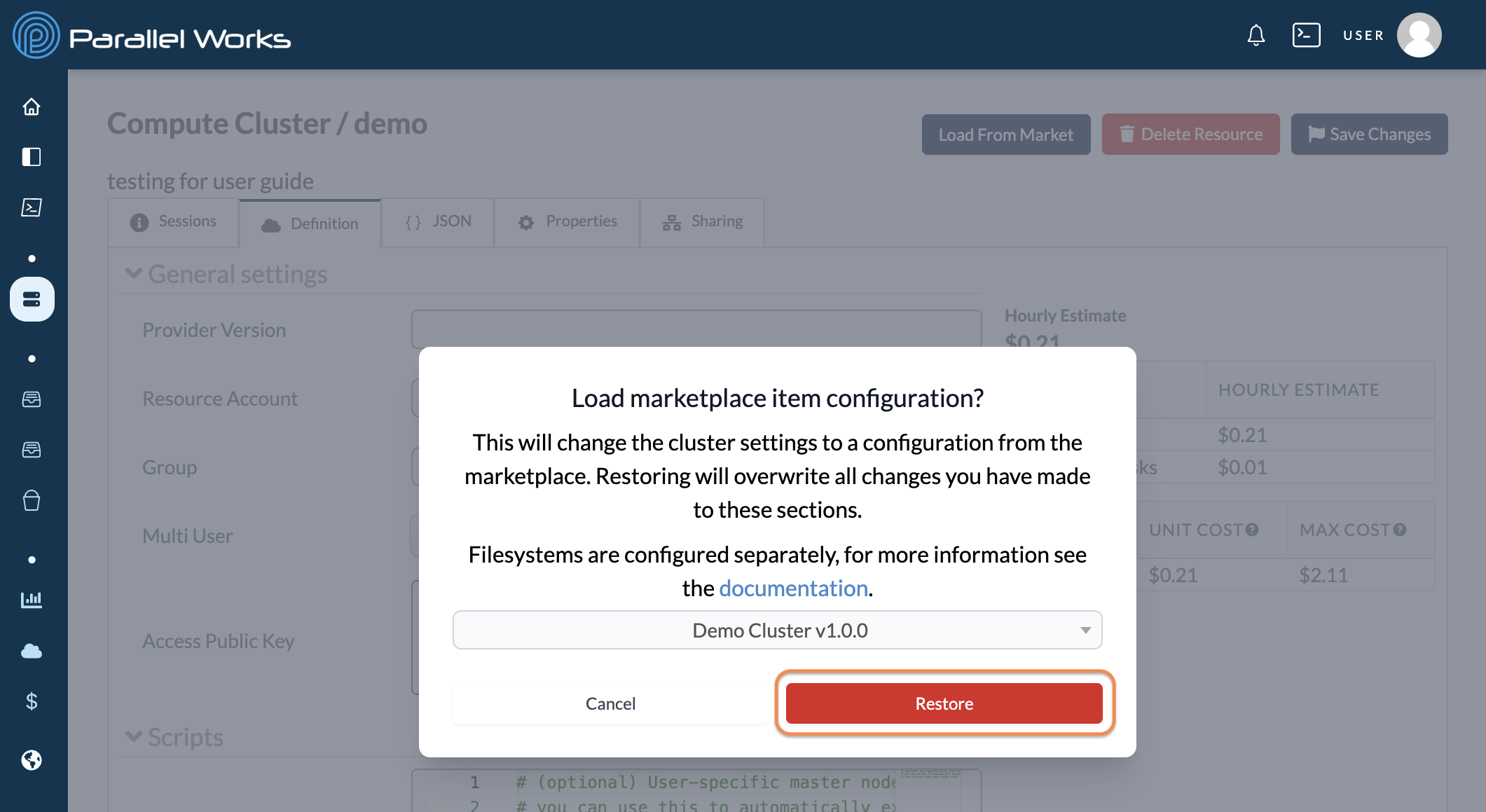
Load From Market
You can load pre-configured settings from existing resources in the Marketplace.
First, add an item from the Marketplace.
Next, create a new resource or navigate to an existing resource's settings. Click Load From Market.
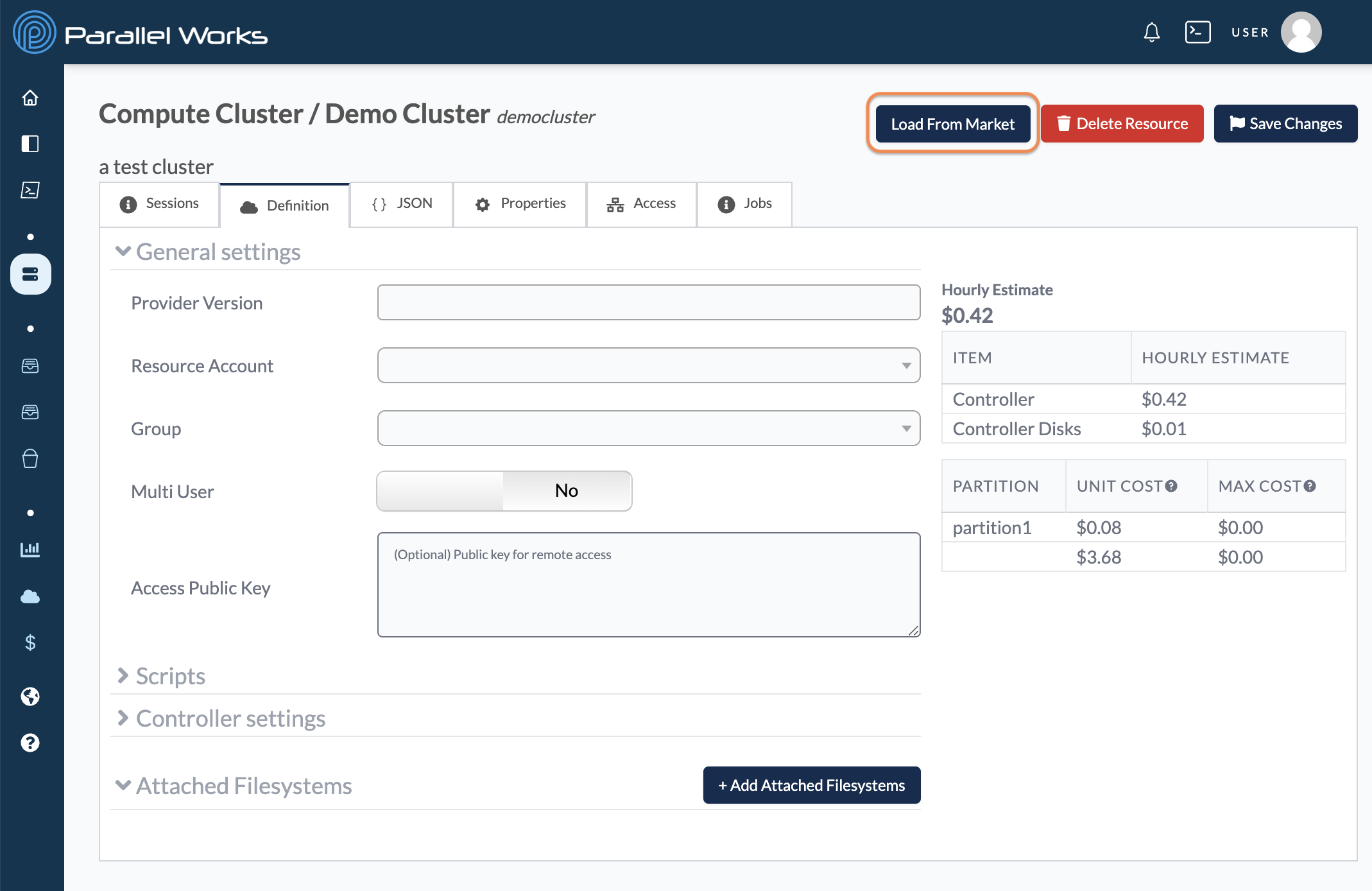
After you click Load From Market, a dialog box will appear. Choose your resource from the dropdown menu, then click Restore.